Power BI Viewer vs Member | A Detailed Comparison
Power BI, a powerful business analytics service by Microsoft, enables organizations to visualize and share insights from their data. Within Power BI, different roles define what users can and cannot do with reports and dashboards.
Two key roles in Power BI are the Viewer and the Member. Understanding the differences between these roles is crucial for managing access and collaboration effectively within an organization. That’s what this article is all about. So, let’s dive right in.
What Are the Different Types of Power BI Users?
Power BI provides various roles to control access and permissions for users within a workspace. The most common roles include Admin, Member, Contributor, and Viewer. Each role has specific permissions that dictate what actions a user can perform.
1. Admin: Manages all aspects of the workspace, including settings, permissions, and content.
2. Member: Collaborates on content creation, sharing, and modification.
3. Contributor: Can create and edit content but has limited permissions compared to a Member.
4. Viewer: Has the least permissions, primarily restricted to viewing content.
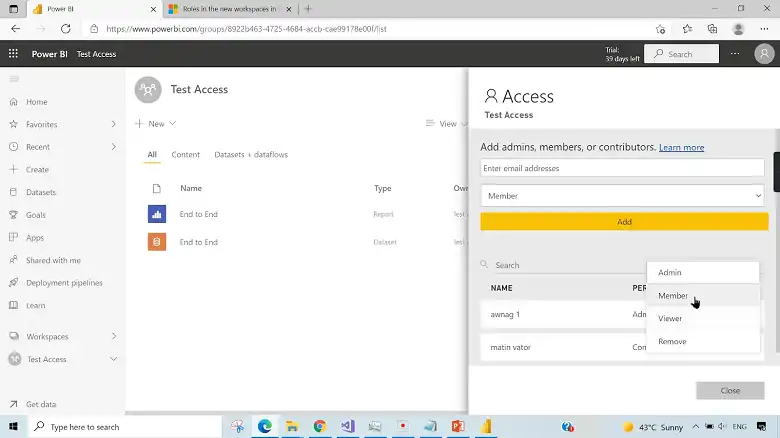
What is Power BI Viewer?
The Viewer role is intended for users who need access to view reports and dashboards without the ability to modify or share them. This role is ideal for stakeholders or executives who require insights from the data without getting involved in the creation or editing process.
Permissions of a Power BI Viewer:
- View Reports and Dashboards: Users can view all reports and dashboards shared with them.
- Interact with Content: Users can filter, drill down, and interact with the visuals to explore the data in the reports.
- Export Data: Depending on the settings, viewers may have the ability to export data from the reports.
- No Edit Rights: Viewers cannot modify, create, or share reports and dashboards.
- No Access to Datasets: Viewers do not have access to the underlying datasets used in the reports.
Consider a scenario where a company’s executive team needs to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) through Power BI dashboards. The executive team is granted the Viewer role, allowing them to view and interact with the dashboards but not change the reports or datasets. This ensures that the data remains consistent and secure while still providing the necessary insights.
What is Power BI Member?
The Member role is designed for users who are actively involved in the creation, modification, and sharing of Power BI content. Members have more permissions than Viewers and can collaborate with others in the workspace.
Permissions of a Power BI Member:
- Create Reports and Dashboards: Members can create new reports and dashboards within the workspace.
- Edit Content: Members can modify existing reports, dashboards, and datasets.
- Share Content: Members can share reports and dashboards with others, including external users if allowed.
- Manage Permissions: Members can manage the access and permissions for reports and dashboards within the workspace.
- Access to Datasets: Members can connect to, view, and modify datasets.
Imagine a business analyst responsible for generating weekly sales reports for the sales team. This analyst is assigned the Member role, allowing them to create, edit, and update reports as new data becomes available. They can also share the reports with the sales team and adjust permissions as needed.
What Is the Difference Between Member and Viewer in Power BI?
The primary differences between the Viewer and Member roles revolve around the level of access and control users have over the content within Power BI.
Content Creation and Editing: Members can create and edit reports, while Viewers can only view and interact with existing content.
Sharing and Permissions: Members can share reports and manage permissions, while Viewers have no control over sharing or permissions.
Dataset Access: Members have access to datasets and can use them to create or modify reports, whereas Viewers do not have direct access to datasets.
The following table highlights the key differences in permissions and capabilities between the Power BI Viewer and Member roles, helping you understand which role to assign based on the user’s needs.
| Feature/Permission | Power BI Viewer | Power BI Member |
| View Reports and Dashboards | Yes | Yes |
| Interact with Content | Yes (filter, drill down, etc.) | Yes (full interactivity) |
| Export Data | Yes (if allowed by report settings) | Yes |
| Create Reports and Dashboards | No | Yes |
| Edit Existing Reports and Dashboards | No | Yes |
| Share Content | No | Yes |
| Manage Permissions | No | Yes |
| Access to Datasets | No | Yes |
| Modify Datasets | No | Yes |
Best Practices for Assigning Power BI Roles
Assigning the appropriate roles within Power BI is essential for maintaining data security and ensuring that users have the necessary access to perform their tasks. Here are some best practices:
Limit Viewer Roles to Stakeholders: Assign the Viewer role to users who only need to view reports and dashboards, such as executives or department heads.
Assign Member Roles to Content Creators: Assign the Member role to users responsible for creating, modifying, and managing content within the workspace, such as data analysts or report creators.
Regularly Review Role Assignments: Periodically review the roles assigned to users to ensure they still align with their responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Power BI Viewer export data?
Yes, depending on the export settings configured by the report owner, a Viewer may have the ability to export data from the report. However, they cannot modify or manage the report itself.
Can a Member role access and modify datasets?
Yes, Members can access, view, and modify datasets within the workspace. They can use these datasets to create or update reports and dashboards.
Is it possible for a Viewer to become a Member?
An Admin or Member with the appropriate permissions can change a user’s role from Viewer to Member within the workspace settings.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the Viewer and Member roles in Power BI is crucial for effective collaboration and data governance within an organization. By assigning roles appropriately, you can ensure that your data is both secure and accessible to those who need it, fostering a productive and efficient work environment.