Power BI Member vs Contributor
Power BI is an essential tool for organizations aiming to harness the power of their data through visualization and reporting. To ensure effective collaboration, Power BI provides different roles within its workspaces. Two key roles that often come into play are Member and Contributor.
Understanding the distinctions between these roles is crucial for anyone involved in managing or contributing to Power BI projects. This article is all about comparing these two roles in terms of advantages, usability, and more.
What Are the Different Types of Power BI Users?
Power BI workspaces allow users to collaborate on reports, dashboards, datasets, and other assets. Each role within a workspace comes with specific permissions that determine what a user can or cannot do. Here’s a quick overview of some common roles:
- Admin: Full control over the workspace, including the ability to add or remove members, assign roles, and manage workspace settings.
- Member: A role with broad permissions to interact with most aspects of the workspace but without full administrative privileges.
- Contributor: A role focused on content creation and management within the workspace but with more limited permissions than a Member.
- Viewer: A role that primarily allows users to view content without making changes.
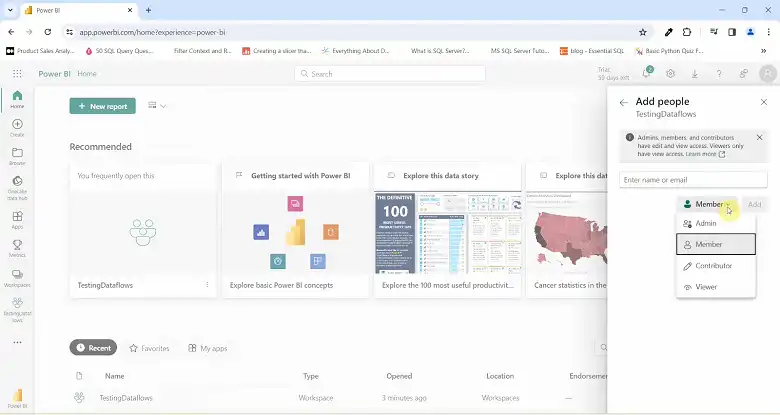
The Role of a Member in Power BI
A Member in a Power BI workspace is someone with extensive permissions, second only to an Admin. Members have the authority to perform a wide range of tasks:
Content Management: Members can create, edit, and delete reports, dashboards, and datasets. They can manage connections to data sources and adjust refresh schedules, ensuring that reports and dashboards remain up-to-date.
Collaboration and Sharing: Members can share their work with others, both within the workspace and, if permissions allow, outside the organization. This makes them key players in the distribution of insights across teams.
User Management: While Members do not have full administrative control, they can manage certain user permissions. For example, they can assign the Contributor or Viewer role to other users, allowing them to dictate who can contribute to or view specific content.
Partial Administrative Capabilities: Members can add new users to the workspace and manage content permissions but cannot make significant changes to workspace settings, like changing its name or transferring ownership.
The Role of a Contributor in Power BI
A Contributor in Power BI focuses more narrowly on content creation and management. Here’s what a Contributor can do:
Creation and Editing: Contributors are responsible for creating and editing reports, dashboards, and datasets. They play a crucial role in developing the content that drives business decisions.
Content Deletion: Contributors can delete the content they create, although they may be restricted from deleting content created by others unless they have additional permissions.
Publishing Within the Workspace: Contributors can publish reports and dashboards for use within the workspace. However, their ability to share content outside the workspace is typically limited unless explicitly granted.
No Role Assignment: Unlike Members, Contributors do not have the authority to assign roles or manage user permissions. Their focus remains on content rather than on broader workspace management.
What Is the Difference Between Contributor and Member in Power BI?
Understanding the differences between these roles can help organizations assign the appropriate permissions to each user, ensuring that they can contribute effectively without overstepping their bounds.
| Feature/Capability | Member | Contributor |
| Content Creation | Create, edit, and delete reports, dashboards, and datasets | Create, edit, and delete their own reports, dashboards, and datasets |
| Sharing and Collaboration | Share content within and outside the organization | Publish content within the workspace; limited external sharing |
| Role Assignment | Can assign Contributor or Viewer roles to others | Cannot assign roles |
| User Management | Manage permissions for certain users | Focused solely on content creation; no user management capabilities |
| Administrative Tasks | Limited admin tasks (e.g., adding users) | No admin tasks; cannot manage workspace settings |
Member vs Contributor: When to Use Each What
Assigning the right role depends on the needs of the project and the responsibilities of the team members:
Member: This role is ideal for users who need to manage both content and user permissions within the workspace. They should have a good understanding of the workspace’s structure and the flow of information, as they play a critical role in both content creation and distribution.
Contributor: Assign this role to users whose primary responsibility is to develop and maintain reports, dashboards, and datasets. They should be experts in data analysis and visualization, focusing on creating content that drives decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a contributor share a report in Power BI?
You can easily share reports and dashboards from your personal workspace. To share content from shared workspaces, you’ll need either Admin or Member permissions. If you have Contributor or Viewer roles, you can still share content if you have specific sharing permissions granted to you.
Can users edit Power BI reports?
To edit and share reports with others, you need a Power BI Pro or Premium Per User (PPU) license. Without this license, you can still create reports but won’t be able to share them.
Conclusion
In Power BI, the distinction between the Member and Contributor roles is crucial for effective workspace management. By understanding these roles, organizations can ensure that users have the appropriate level of access to perform their tasks effectively, maintaining a balance between collaboration and control.
Whether you’re a Member with broad responsibilities or a Contributor focused on content creation, both roles are integral to the success of Power BI projects.