How to Set PYTHONPATH | Step-by-Step Guide
Setting the PYTHONPATH environment variable is essential for Python developers who want to manage where Python looks for modules and packages. This is particularly useful when working on projects that have dependencies spread across multiple directories or when using custom modules.
Understanding PYTHONPATH
PYTHONPATH is an environment variable that you can set to add additional directories where Python will look for modules and packages. By default, Python searches for modules in the directories listed in sys.path, which includes the directory containing the input script, the standard library directories, and the site-packages directory.
Methods to Set PYTHONPATH
Temporarily Set PYTHONPATH in the Command Line
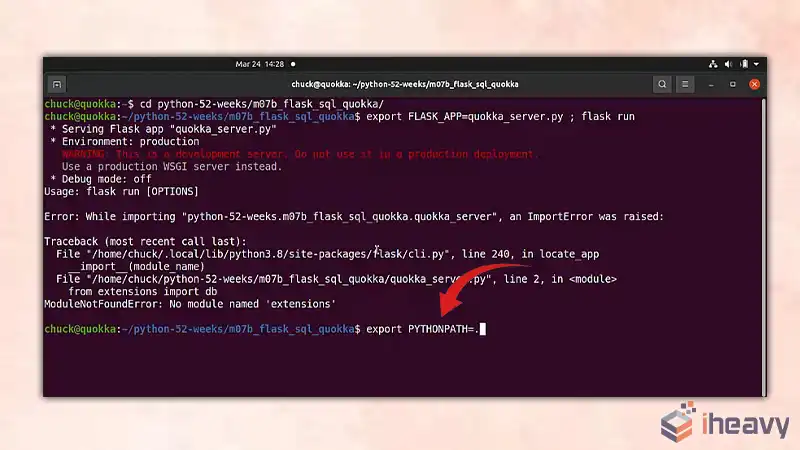
You can set PYTHONPATH temporarily in your command line session. This method is useful for testing or running scripts from the command line.
On Windows:
set PYTHONPATH=C:\path\to\your\directory
python your_script.py
On macOS and Linux:
export PYTHONPATH=/path/to/your/directory
python your_script.py
Permanently Set PYTHONPATH in the Environment Variables
To set PYTHONPATH permanently, you need to modify your system’s environment variables. This ensures that PYTHONPATH is set every time you start a new session.
On Windows:
Open the Start Menu and search for “Environment Variables”.
Click on “Edit the system environment variables”.
In the System Properties window, click on “Environment Variables”.
Under “System variables”, click “New” to create a new variable.
Set the variable name to PYTHONPATH and the variable value to your desired directory path.
Click “OK” to save the changes.
On macOS and Linux:
Open your terminal.
Open your shell profile file in a text editor. This could be ~/.bashrc, ~/.bash_profile, ~/.zshrc, etc., depending on your shell.
Add the following line to the file:
export PYTHONPATH=/path/to/your/directory
Save the file and run the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.bashrc # or source ~/.bash_profile, source ~/.zshrc
Setting PYTHONPATH in a Python Script
You can also set PYTHONPATH within a Python script using the sys module. This method is useful when you want to programmatically manage your module search paths.
import sys
import os
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(‘/path/to/your/directory’))
# Now you can import your custom modules
import your_module
Example Code
Here’s an example of setting PYTHONPATH temporarily and permanently on a Unix-like system:
Temporarily:
export PYTHONPATH=/home/user/my_python_modules
python my_script.py
Permanently:
Open .bashrc:
bash
Copy code
nano ~/.bashrc
Add the line:
export PYTHONPATH=/home/user/my_python_modules
Save and close the file, then apply the changes:
source ~/.bashrc
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I set multiple paths in PYTHONPATH?
Yes, you can set multiple paths in PYTHONPATH by separating them with a colon (:) on Unix-like systems or a semicolon (;) on Windows.
Does setting PYTHONPATH affect all Python versions?
Setting PYTHONPATH affects all Python versions installed on your system. If you want to set it for a specific version, you can use virtual environments.
How can I check if PYTHONPATH is set correctly?
You can check the current PYTHONPATH value by running the following command in Python:
import sys
print(sys.path)
Conclusion
Setting the PYTHONPATH environment variable is a powerful tool for Python developers, allowing greater flexibility in managing and organizing Python modules and packages. Whether you need to set it temporarily for testing or permanently for consistent usage across sessions, the methods outlined in this article will help you achieve your goals. By understanding and utilizing PYTHONPATH, you can streamline your development process and maintain a cleaner project structure.

![How to Fix java.lang.NullPointerException | [Answered]](https://www.iheavy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/How-to-Fix-java.lang_.NullPointerException-768x432.webp)