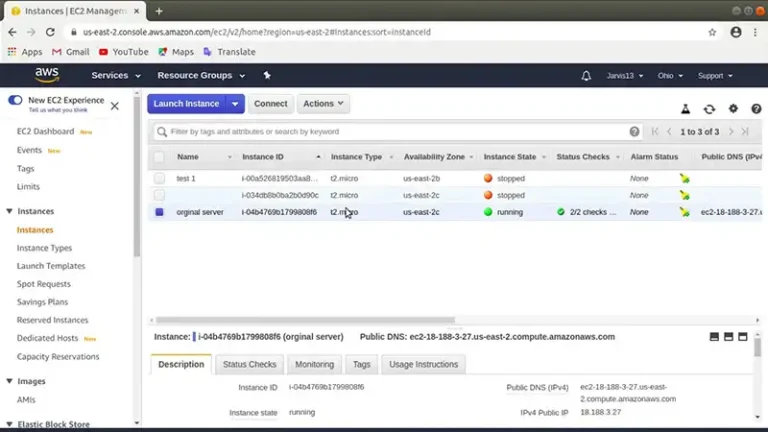
How to Migrate On-Premise Server to AWS Step by Step | 8 Step Guideline
Migrating an on-premise server to AWS involves eight key steps: assess and plan, design AWS infrastructure, set up AWS environment, migrate data, migrate applications, switch over and validate, optimize and maintain post-migration, and decommission on-premise infrastructure. This comprehensive process covers everything from initial analysis to final validation, ensuring a smooth transition to AWS.
This step-by-step guide aims to demystify the process, providing a comprehensive roadmap for migrating your on-premise server infrastructure to AWS seamlessly.
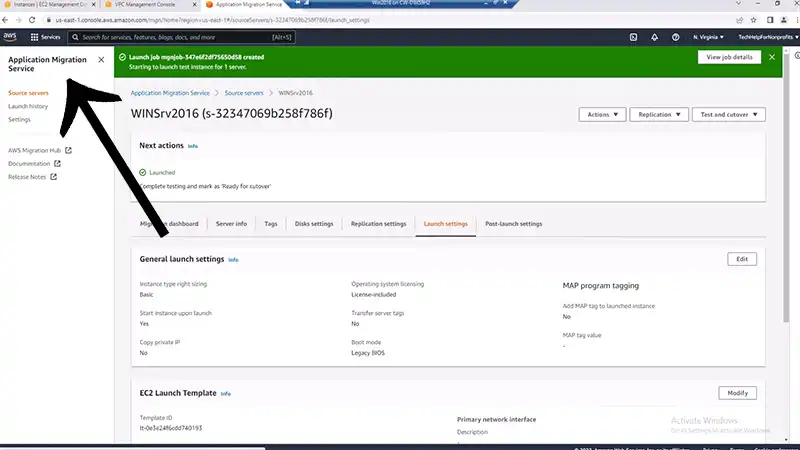
Step-By-Step Process of Migrating On-Premise Server to AWS
Migrating an on-premise server to AWS involves several steps to ensure a smooth transition of your infrastructure. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Assessment and Planning
1. Inventory Analysis: Take stock of your current on-premise infrastructure, noting hardware specifications, software configurations, dependencies, and data volumes.
2. Performance Analysis: Evaluate server performance metrics to determine AWS instance types that match or exceed the existing capabilities.
3. Cost Analysis: Estimate the costs associated with AWS resources required for migration and ongoing operation.
Step 2: Designing the AWS Infrastructure
1. Selecting AWS Services: Choose AWS services like EC2 instances, RDS, S3, etc., to replicate your on-premise setup.
2. Architectural Design: Create an architecture diagram outlining how components will be replicated or restructured in AWS.
3. Network Configuration: Plan VPC, subnets, security groups, and network settings to mirror your existing setup.
Step 3: Setting Up AWS Environment
1. Create an AWS Account: Sign up for an AWS account if you don’t have one.
2. Set Up Networking: Configure VPC, subnets, internet gateways, route tables, and security groups based on your design.
3. Set Up IAM: Create IAM users, roles, and policies to manage access control.
Step 4: Data Migration
1. Data Backup: Take a full backup of your on-premise data before the migration.
2. Transfer Data to AWS: Use services like AWS Storage Gateway, AWS Snowball, or direct transfer methods to move data to AWS.
3. Data Validation: Ensure data integrity and consistency after migration.
Step 5: Application Migration
1. Replicate Applications: Install and configure applications on AWS instances as per the design.
2. Testing: Conduct thorough testing of applications in the AWS environment to ensure they function correctly.
3. Migration Validation: Verify that all applications are working as expected in the AWS setup.
Step 6: Switch Over and Validation
1. Cut Over to AWS: Redirect traffic from the on-premise server to the AWS resources.
2. Monitor and Validate: Continuously monitor performance, security, and functionality to confirm the successful migration.
3. Rollback Plan: Have a rollback plan in case of unforeseen issues during or after migration.
Step 7: Post-Migration Optimization and Maintenance
1. Optimize Resources: Fine-tune AWS resources for performance and cost-efficiency.
2. Backup and Disaster Recovery: Set up backup and disaster recovery mechanisms in AWS.
3. Documentation: Update documentation with the new AWS setup for future reference and troubleshooting.
Step 8: Decommissioning On-Premise Infrastructure
1. Validation: Ensure all data and applications are fully functional in AWS before decommissioning the on-premise servers.
2. Shutdown On-Premise Servers: Once everything is validated and working in AWS, decommission the on-premise servers.
Importance of Migrating On-Premise Server to AWS
Migrating on-premise servers to AWS holds significant importance in today’s dynamic business landscape. Here are key points highlighting its importance:
Scalability and Flexibility
AWS offers unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to effortlessly scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility eliminates the constraints of physical hardware, enabling seamless adjustments to accommodate growth or fluctuations in workload.
Cost Efficiency
Shifting to AWS often results in cost savings by reducing upfront hardware investments and operational expenses associated with maintaining on-premise infrastructure. Pay-as-you-go pricing models and the ability to optimize resource usage contribute to substantial cost efficiencies.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
AWS provides robust security measures and compliance certifications, ensuring data protection and regulatory adherence. Advanced security features, encryption protocols, and compliance frameworks empower businesses to bolster their security posture.
Global Accessibility and Reliability
With AWS’s global infrastructure, businesses gain access to a network of data centers worldwide. This global presence ensures high availability and reliability, reducing downtime risks and enhancing accessibility for users across various regions.
Innovation and Agility
AWS continually introduces new services and technologies, fostering innovation and agility for businesses. Leveraging cutting-edge tools and services allows for faster development cycles, experimentation, and quicker time-to-market for new initiatives.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Migrating to AWS enables robust disaster recovery and business continuity strategies. Features like data replication, automated backups, and failover mechanisms minimize downtime and mitigate risks associated with unforeseen events.
Future-Proofing IT Infrastructure
Transitioning to the cloud future-proofs IT infrastructure. It ensures readiness to adopt emerging technologies, facilitates easier integration with third-party tools, and enables rapid adaptation to evolving business needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should I migrate my on-premise server to AWS?
Migrating to AWS offers scalability, cost-efficiency, enhanced security, and accessibility to a wide array of services. It enables businesses to leverage cloud capabilities and reduce hardware maintenance costs.
Which AWS services are commonly used for server migration?
AWS offers services like AWS Server Migration Service (SMS), AWS Database Migration Service (DMS), AWS Snow Family for large-scale data transfer, and AWS Database Freedom for database migrations.
What are the security considerations during server migration to AWS?
Ensure secure data transfer using encryption, implement access controls, configure AWS security groups and network ACLs, and regularly update security measures based on AWS best practices.
Conclusion
Migrating on-premise servers to AWS can significantly enhance an organization’s agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By following this step-by-step guide and leveraging AWS tools and services, businesses can navigate the migration process seamlessly while minimizing disruptions and maximizing the benefits of cloud computing.