How Does AWS Billing Work?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a vast array of cloud computing services that cater to different business needs. Understanding AWS billing is crucial for managing costs effectively and avoiding unexpected charges.
AWS billing works on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning users pay only for the services they use, with no upfront costs or long-term commitments. Here’s a detailed look into how AWS billing operates.

How Does AWS Charge Its Customers?
AWS uses a flexible pricing model based on several key principles:
- Pay-as-you-go: You pay for the compute, storage, and other resources you use without upfront costs.
- Save when you reserve: You can save by committing to AWS services for a longer duration through Reserved Instances (RIs) or Savings Plans.
- Pay less by using more: AWS offers volume-based discounts and tiered pricing for many services.
AWS pricing is transparent, with detailed documentation available for each service. Prices are generally based on the amount of resources consumed, such as compute hours, storage space, and data transfer.
Key Components of AWS Billing
AWS billing is comprised of several key components that help users understand and manage their costs:
AWS Billing Dashboard: The AWS Billing and Cost Management Dashboard provides an overview of your current charges and a forecast of future costs. It offers insights into your spending patterns and helps you understand your AWS usage.
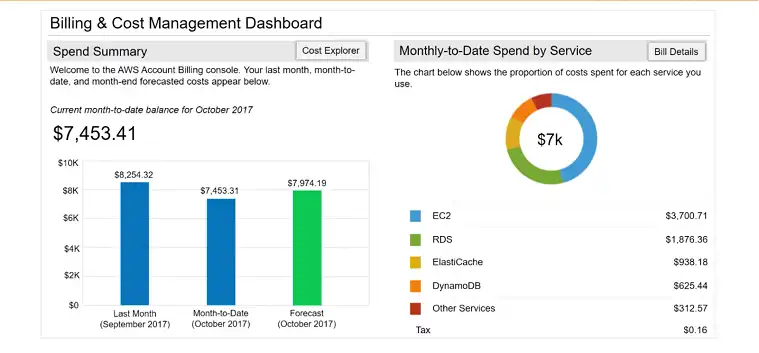
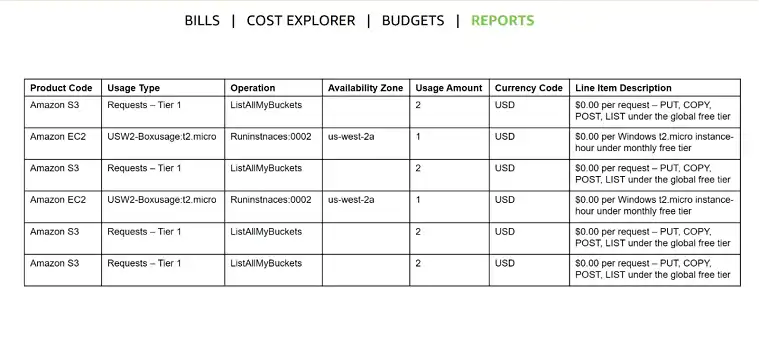
Cost and Usage Reports: AWS Cost and Usage Reports (CUR) provide detailed information about your AWS usage and costs. These reports can be customized to show cost allocation, which helps in managing and optimizing costs across different AWS services.
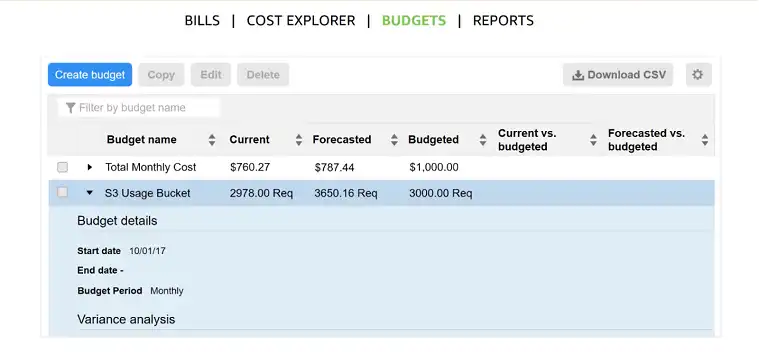
Budgets and Alarms: AWS Budgets allows you to set custom cost and usage budgets that alert you when your usage exceeds your budgeted amount. This helps prevent unexpected charges and keeps your spending in check.
Cost Explorer: AWS Cost Explorer provides a user-friendly interface for analyzing your AWS costs. You can visualize your cost data with graphs and filters to identify trends and areas where cost optimization might be necessary.
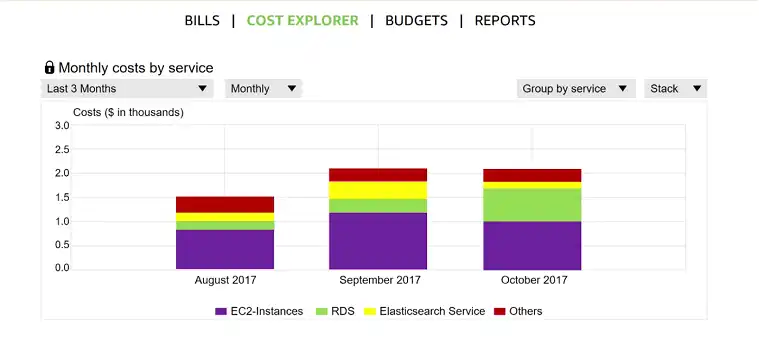
How Does Amazon AWS Billing Work?
AWS offers several pricing models that cater to different usage needs:
On-Demand: Pay for compute or database capacity by the hour or second with no long-term commitments. This model is ideal for short-term, irregular workloads that cannot be interrupted.
Reserved Instances: Make a commitment to use AWS for a one- or three-year term in exchange for a significant discount on hourly charges compared to On-Demand pricing. This is ideal for steady-state workloads.
Savings Plans: A flexible pricing model that offers lower prices compared to On-Demand pricing, in exchange for a commitment to a consistent amount of usage (measured in $/hour) for a one- or three-year term.
Spot Instances: Purchase unused compute capacity at discounted rates, which can be as much as 90% less than On-Demand prices. Spot Instances are ideal for fault-tolerant, flexible applications.
Free Tier: AWS provides a free tier offering limited use of certain services at no cost. This is ideal for new customers to explore AWS services without incurring costs.
What Is Amazon’s Billing Cycle?
AWS billing operates on a monthly cycle. At the end of each month, AWS generates an invoice for the services consumed during that month. The invoice includes a detailed breakdown of costs for each service, usage type, and region.
Monthly Invoicing: Invoices are available in the AWS Billing Dashboard and can be downloaded in PDF format. You can also enable billing alerts to notify you when a new invoice is generated.
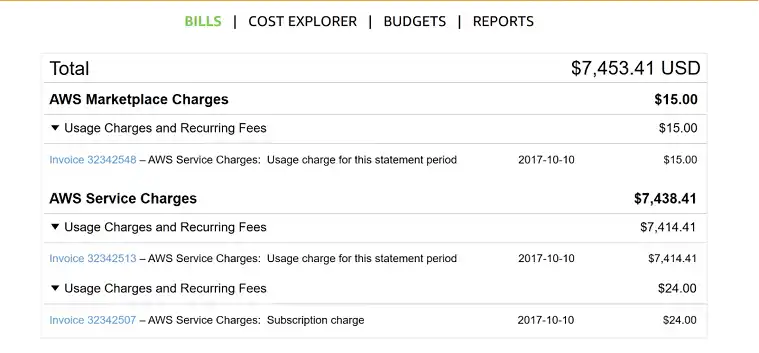
Payment Methods: AWS accepts several payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and ACH direct debit. Enterprise customers can also arrange for invoicing and purchase orders.
Managing AWS Costs
To effectively manage AWS costs, it’s important to regularly monitor usage and take advantage of cost-saving options:
Right-Sizing Resources: Regularly review your resource usage to ensure you’re not over-provisioned. Rightsizing involves selecting the appropriate instance size and storage type based on your workload requirements.
Utilizing Cost Management Tools: Use AWS Budgets, Cost Explorer, and the Cost and Usage Report to track spending, forecast future costs, and identify areas for optimization.
Leveraging Discounts: Make use of Reserved Instances, Savings Plans, and Spot Instances to reduce costs. Evaluate your workload patterns to decide the best pricing model for your needs.
AWS Free Tier and Cost Optimization Programs: AWS offers several free tier options and cost optimization programs to help you try AWS services and learn best practices for cost management.
AWS Support Plans and Billing Assistance
AWS offers several support plans that include billing assistance and cost optimization guidance:
Basic Support: Free of charge, offering 24/7 access to customer service, documentation, whitepapers, and support forums.
Developer Support: Designed for users experimenting with AWS, including support for basic technical questions and best practices guidance.
Business Support: Provides access to a full range of AWS services, including billing and account support, third-party software support, and access to AWS Trusted Advisor for cost optimization.
Enterprise Support: Includes all Business Support features plus a dedicated Technical Account Manager (TAM), proactive guidance, and programmatic access to best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the AWS Free Tier?
The AWS Free Tier provides a limited amount of usage for AWS services at no cost. It includes services such as Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, and AWS Lambda, allowing new users to explore AWS for free for 12 months.
How can I avoid unexpected charges on my AWS bill?
To avoid unexpected charges, set up AWS Budgets to monitor your spending and receive alerts. Use the AWS Cost Explorer to analyze your usage patterns and identify cost-saving opportunities. Always monitor your AWS Free Tier usage, as exceeding the limits will incur charges.
What happens if I don’t pay my AWS bill?
If you fail to pay your AWS bill on time, AWS will repeatedly notify you via email, urging you to settle your account. If the payment remains outstanding after three months, your account may be terminated, and your credit card could be flagged.
Conclusion
By understanding how AWS billing works and utilizing the tools and features available, you can effectively manage and optimize your AWS costs, ensuring you get the most value from your cloud investment.

![[Answered] How To Migrate A Website To AWS?](https://www.iheavy.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/How-To-Migrate-A-Website-To-AWS-768x431.webp)