Installing MongoDB 4.2 on Ubuntu | A Step-by-Step Guide
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database that offers a flexible and scalable solution for managing unstructured data. Installing MongoDB 4.2 on Ubuntu is a straightforward process, but it requires a few steps to ensure a smooth setup. In this guide, we’ll walk through the process of installing MongoDB 4.2 on Ubuntu and provide tips for configuring and verifying the installation.
Update Package Repository
Before installing MongoDB, it’s essential to update the package repository on your Ubuntu system to ensure you have access to the latest versions of software packages:
sudo apt update
Import MongoDB GPG Key
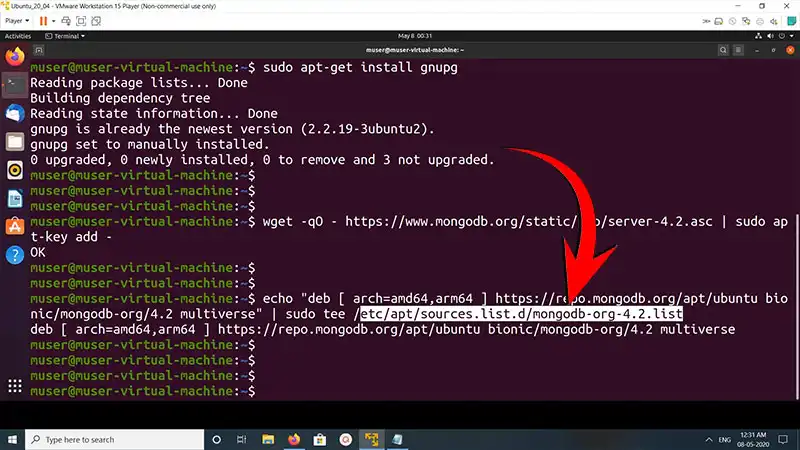
Next, import the MongoDB GPG key to ensure the authenticity of the MongoDB packages:
wget -qO – https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.2.asc | sudo apt-key add –
Add MongoDB Repository
Add the MongoDB repository to your system’s list of package sources:
echo “deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.2 multiverse” | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.2.list
Install MongoDB
Now, install MongoDB 4.2 using the following apt command:
sudo apt install -y mongodb-org
This command installs the MongoDB package along with its dependencies.
Start MongoDB Service
After the installation is complete, start the MongoDB service using the systemctl command:
sudo systemctl start mongod
Verify MongoDB Installation
You can verify that MongoDB is running correctly by checking its status with systemctl:
sudo systemctl status mongod
If MongoDB is running, you should see an active (running) status indication.
Enable MongoDB Service
To ensure that MongoDB starts automatically every time your system boots, enable the MongoDB service:
sudo systemctl enable mongod
Access MongoDB Shell
You can access the MongoDB shell to interact with the database by running the following command:
mongo
This command connects you to the MongoDB instance running on your local system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can I install MongoDB 4.2 on versions of Ubuntu other than Bionic (18.04)?
Yes, MongoDB provides repositories for different versions of Ubuntu. Simply replace “bionic” in the repository URL with the codename of your Ubuntu version.
How can I uninstall MongoDB from my Ubuntu system?
To uninstall MongoDB, you can use the apt command with the purge option to remove the MongoDB package and its configuration files:
sudo apt purge mongodb-org
Is it necessary to add the MongoDB GPG key before installing MongoDB?
Adding the MongoDB GPG key ensures the authenticity of the MongoDB packages and helps prevent the installation of malicious software. It is recommended to import the GPG key before installing MongoDB.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can install MongoDB 4.2 on your Ubuntu system and start working with this powerful NoSQL database. Remember to periodically check for updates and security patches to keep your MongoDB installation secure and up to date.